
Overview
More Admin tools
- PortCheck - Check TCP ports in Windows 11
- Remote Device Manager Windows 11 - DeviceTool
- USBSecure Enterprise - USB Port Security Software
- DisplayTool - Tail for Windows 11
Articles
- How to wake up computers with a free Wake on Lan tool
Downloads
PingTool Help
Latest version is 4.1.0.48 (05-Apr-2024). Please update to this version. Why?
Bug in Version 4.0.0.32: .Net Framework 3.5 is required for TCP portcheck >>> Solve the problem
Tutorial PingTool 4.1
PingTool is the small, powerful tool for administrators and network admins. Besides adhoc ping monitoring, it also offers the possibility to check TCP ports and to wake up computers via Wake-on-Lan (Magic Packet).
Content
► What's new in version 4.1.0.48
► What's new in version 4.0.0.32
► Ping
► Object discovery
► Snapshots
► Wake-on-Lan
► TCP port check
► Keyboard shortcuts
► Backup / Restore
► Transfer to another PC
► Repository
► Mail notification
► User-defined actions
► Commands
► Dashboard
► Command line
► Network installation
► Rollout via software
distribution
What's new in version 4.1.0.48 (latest version)?
► Commands: Execute user-defined commands from PingTool
► Own IP address in window title (via settings)
► Bugs fixed:
- Request for installation
of .NET Framework 3.5 on some systems when checking TCP ports
- Crash when creating a snapshot with
English language settings
- Not allowed default name when performing a
backup with English language settings
- Sorting by description works again
- Error when repeatedly adding objects with
variable host names
- Filter for selected objects now works
What's new in version 4.0.0.32 (March 2024)?
Very extensive improvements have been made with version 4.0. But you will recognize the PingTool :).
► TCP PortCheck integrated in GUI
► Simplified saving and loading of configurations
► Import from Excel or text files
► E-mail notification
► Real-time log (complete or for single objects)
► Correct sorting by IP addresses
► Ping interval adjustable (1 - 120 sec.)
► Repositories for professional use --> read more about repositories...
► Dark mode
► Adjustable double-click action
► Cloning objects
► Adding objects with variable host names
► Backup / restore of all configurations and settings
► Dashboard
► User-defined actions --> read more about user-defined actions...
► PingMonitor threshold adjustable
► Improved performance
► ...and many, many small improvements
What was new in version 3.0.0.24 (March 2022)?
► Improved performance
PingTool had the problem in version 2 that with many objects to be pinged (e.g. 200 objects) the CPU load increased strongly. This has been extremely improved.
► Better GUI
Up to version 2, the GUI often had "hangs" in usability, especially with objects that could not be resolved via DNS. This has been fixed.
► Saveable configurations
Configurations can now be saved and loaded at will.
► Improved filtering options
The filtering of objects has been greatly improved. Among other things, it is now possible to filter for "responding" or "non-responding" objects with one click.
► "Important TCP ports" can be saved
The important TCP ports can now be adjusted by the user, because every admin considers other TCP ports "important". Simply right click on an object --> PortCheck on objects --> Change.
► Shutdown computers
In addition to "waking up the computer" via Wake-On-Lan, Windows computers can now also be shut down. Appropriate permissions are required.
► Pathping and "PortCheck - important Ports"
In the context menu (right mouse button) there are now additional items "Pathping" and "PortCheck - important ports" for even faster usability.
>> Download PingTool latest version now
What was new in version 2.0.0.14?
► Portable tool
PingTool is no longer offered as MSI package for download, but as ZIP file. So just unzip and copy it to a directory - for example C:\Program Files (x86)\PingTool - and get started.
► Better filtering option
In the "Filter" field at the top right, you can now filter for multiple objects, separated by a '|' sign.
► Mousewheel
The display size can now be changed via Ctrl + mouse wheel.
► TCP port check via command line
The TCP port check can now (alternatively) be called directly as an interactive command line tool. The comfortable option via right mouse button is also available.
► New files path
The user's PingTool files are now located under %localappdata%\PingTool instead of %localappdata%\Temp\PingTool because the Temp directory is regularly deleted in some companies.
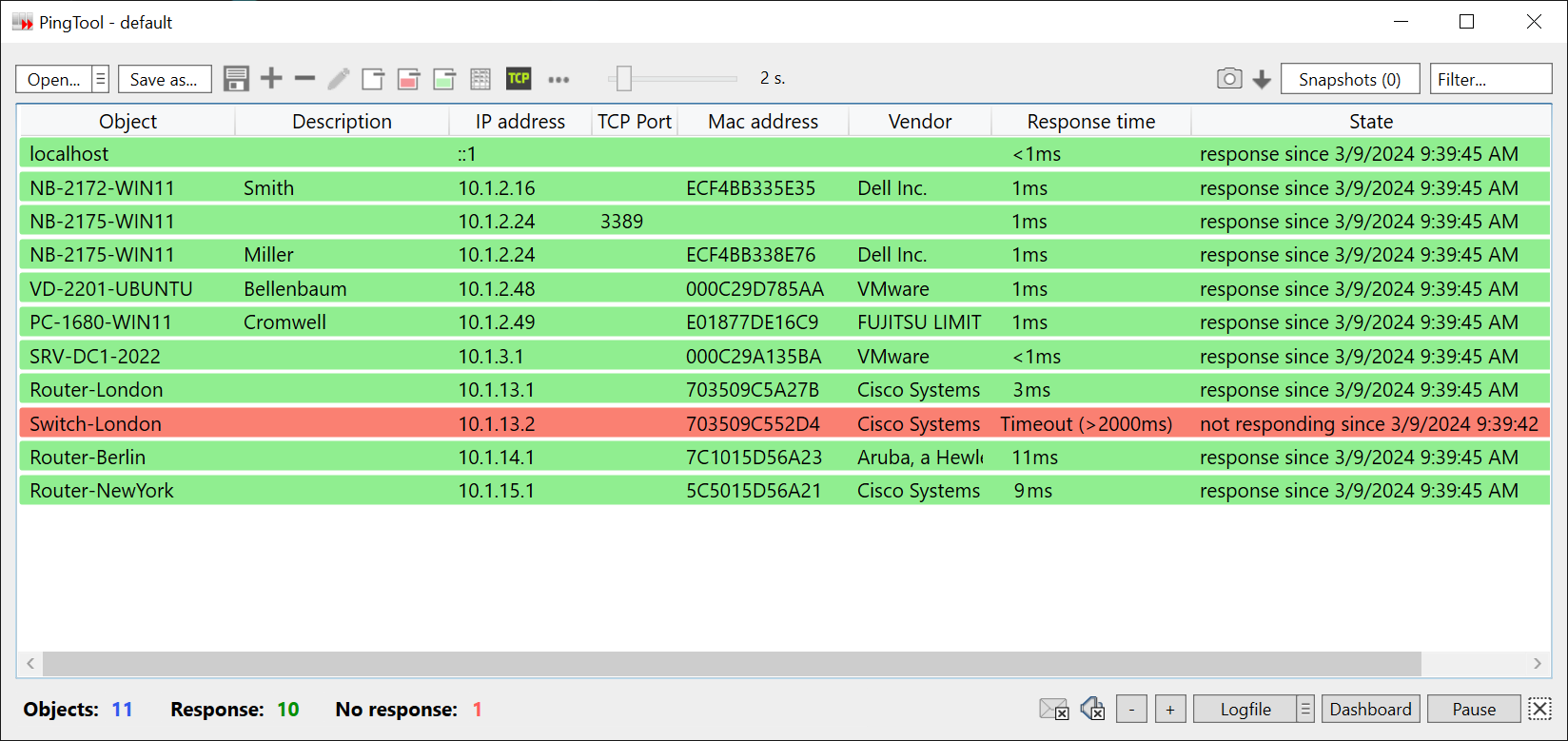
Ping
PingTool displays the availability status of network objects in real
time by pinging them periodically. The default ping of the operating
system is used for this purpose.
Add new objects
Adding new objects is done via the + sign in the upper left corner.
Add objects from another software
Each object in PingTool corresponds to a file in the
%localappdata%\PingTool\Objects directory ("Everything is a file").
This gives you the possibility to add objects also from another software
or by script.
Transfer objects from PingTool to PingTool
To transfer objects from one PingTool instance - for example from an RDP session - to another, proceed as follows: Create a snapshot with the "arrow down" icon, copy the complete text content to the clipboard with Ctrl-A and Ctrl-C and paste it in the other PingTool instance with Ctrl-V.
Object discovery
Discovering objects is done via the + sign --> Scan area. A
maximum of 255 objects can be discovered at once. When discovering, it
is also possible to determine the host names.
Determine Mac addresses and manufacturers
Click the grid icon at the top left to discover the Mac addresses and vendor names of the existing objects. Note that Mac address discovery works only in your own subnet. The Mac addresses from other subnets are not visible due to the network.
Snapshots
PingTool offers you the possibility to create one-time or recurring snapshots of the reachability states (responding / not responding) of your objects. A snapshot consists of a text file that contains readable information. To create snapshots on a regular basis, activate the checkbox in the upper right corner and specify the time interval in seconds.
Wake-on-Lan
PingTool can wake up computers in the network via Wake-On-Lan. For
this purpose, the Magic Packet is sent. Network cards that listen to it
are then able to start the computer.The Mac address is used for
addressing. This means that computers can only be woken up with PingTool
if the Mac address is available. In the own subnet the Mac addresses can
be determined automatically (see "Discovern objects").
To wake up a computer, simply right-click on the object and select "Wake
up object(s) (Wake-On-Lan)". The computer to be woken up must be
prepared for Wake-On-Lan. Learn how to safely get a Wake-On-Lan enabled
network in 8 steps in the
Wake
On Lan Windows 10 tutorial.
Wake-on-Lan to other subnets
The network must be specially configured to wake up computers in other subnets. The routers must allow Wake-On-Lan packets to pass through. Important: The broadcast address of the target network is needed, which can be calculated from the IP address in combination with the subnet mask. PingTool takes care of this for you - you just have to set the correct subnet mask during wake-up.
TCP port check
You can enter a TCP port to be checked for each object. If no TCP port is entered, ping is executed (ICMP).
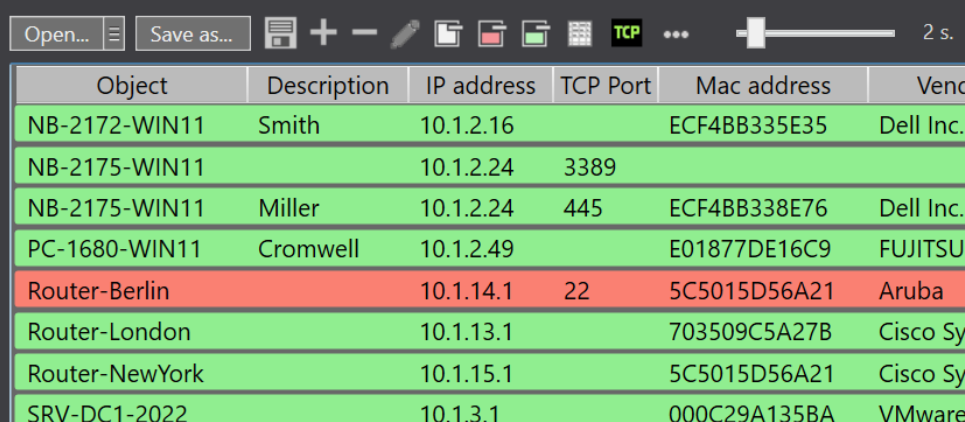
The command line tool PortCheck.exe is integrated in PingTool, so you can comfortably check every object in PingTool if one or more TCP ports are responding. Learn here how to check a TCP port directly with the PortCheck tool.
To check a TCP port of a network object, right-click on the object and select "PortCheck on object(s)". Alternatively, you can also click on the "TCP" sign in the upper left corner to start PortCheck as an interactive command line tool.
Keyboard shortcuts
For quick work the following keyboard shortcuts can be used in
PingTool:
|
Ctrl-+ |
Add objects |
|
Del |
Delete selected objects |
|
Ctrl-O |
Open configuration |
|
Ctrl-S |
Save configuration |
|
Ctrl-F |
Filter |
|
Ctrl-R |
Show only red objects |
|
Ctrl-G |
Show only green objects |
|
Ctrl-Q |
Show all objects |
|
Ctrl-8 |
Decrease font size |
|
Ctrl-9 |
Increase font size |
|
Ctrl-0 |
Font size 100% |
|
F10 |
Run Dashboard |
|
F11 |
Full screen |
|
F12 |
Open realtime log |
Backup / Restore
As of PingTool 4, it is possible to perform backups and restores via the three-dots menu (...). Read more about manual backups and restores...
Transfer to another PC
To move to another PC, simply make a backup and then restore to the new PC (see above).
Repository
Create a central repository for configurations. In larger networks, this enables several administrators to access the same, centrally maintained configuration files without searching. A configuration file contains a list of objects that are pinged by PingTool. Configuration files and repository files are opened via the "Open" button (or Ctrl-O) and have the file extension .cfg. Read more...
Mail notification
PingTool can send mails if an object does not respond. Read more...
User-defined actions
By default, PingTool already offers many options for executing certain actions on one or more objects. Using the context menu (right mouse button), objects can be pinged via the command line, an RDP session can be established or a connection via HTTPs, for example.
However, there are often additional company-specific actions that would be desirable. This is where user-defined actions come into play: create your own actions that can be executed with the right mouse button on one or more objects. Read more...
Commands
The "Commands" provide a way to execute frequently
used network commands with a single click. These are commands that would
otherwise have to be laboriously executed via the command prompt or with
many mouse clicks. One example of this is clearing the DNS cache with
ipconfig /flushdns. A command that every network user
knows and that you need from time to time.
So how do I proceed if I want to save the command in the PingTool?
Read
more or
watch the short video...

A short video about "Commands". Click on the bitmap to watch.
Dashboard
The PingTool Dashboard provides a simplified view of the pinged objects. It was specially developed to give administrators a good overview of the network in difficult environments. These can be industrial environments, data center rooms or network basements where hardware is being rebuilt or cabling is being renewed.

The Dashboard always runs in addition to the actual PingTool and displays the monitored objects in container form with a green and a red area.
The PingTool Dashboard offers the following functionality:
-
Presentation of objects in simplified form
-
Scaling font size
-
Switching to full screen with F11
-
"Always on top" function
-
Own log for subsequent analysis (F12)
The Dashboard is characterized by the fact that you only need a few mouse clicks or keystrokes. Once it has been started, you can switch to full screen by pressing F11. The scaling font size provides an easy-to-read overview even in difficult environments.
Command line
PingTool can be started via the command line (or via a shortcut) in order to specify some settings directly:
PingTool.exe <MyConfigFile>
or
PingTool.exe -config:<MyConfigFile> -interval:<MyInterval> -rundashboard
In the first case, only the configuration file to be opened is specified (important: with the ending .cfg). In the second case, the configuration file, the interval (possible values: 1, 2, 3, 5, 10, 30, 60 or 120) and the information as to whether the PingTool Dashboard should be started are specified.
Examples:
PingTool.exe "%localappdata%\PingTool\Configs\All Routers.cfg"
PingTool.exe -interval:10
PingTool.exe -config:"%localappdata%\PingTool\Configs\Production machines.cfg" -interval:5 -rundashboard
PingTool.exe -config:"O:\PingTool\Repository - All Switches.cfg" -rundashboard
Network installation
PingTool can be started directly from a network drive. This means that several administrators can use PingTool without having to worry about software distribution. To do this, proceed as follows:
-
Download the current PingTool version (zip file) and unzip it.
-
Copy the files to a network folder.
-
Customize the PingTool.ini file. If available, enter a RepositoryPath.
-
Start PingTool.exe.
Rollout via software distribution
In larger environments, it makes sense to roll out software via a software distribution system. As PingTool is portable, requires no installation routine and makes no registry entries, software distribution is limited to a pure copying process and the creation of a link. Simply edit the PingTool.ini file (enter RepositoryPath, if available) and ensure that all files end up in the C:\Program Files (x86)\PingTool folder, for example. Then add a shortcut to the PingTool.exe - done.
Bug in Version 4.0.0.32: .Net Framework 3.5 is required for TCP
portcheck
In version 4.0.0.32 it can happen in certain constellations that the installation of .Net Framework 3.5 is required when you want to check a TCP port via the GUI.
Solution:
The installation of .Net Framework 3.5 is not necessary! Only a tiny configuration file called PortCheck.exe.config is missing.
You can create the file as follows: Copy the PingTool.exe.config file and rename the copy to PortCheck.exe.config. This solves the problem.
Of course, a patched version will be available for download shortly.
Software: PingTool
Category: : PingTool Help / PingTool Tutorial /
PingTool Manual
Go to Ping Tool homepage